
In the United States, the DSM serves as a universal authority for the diagnosis of psychiatric disorders.
Dsm 5 schizophrenia manual#
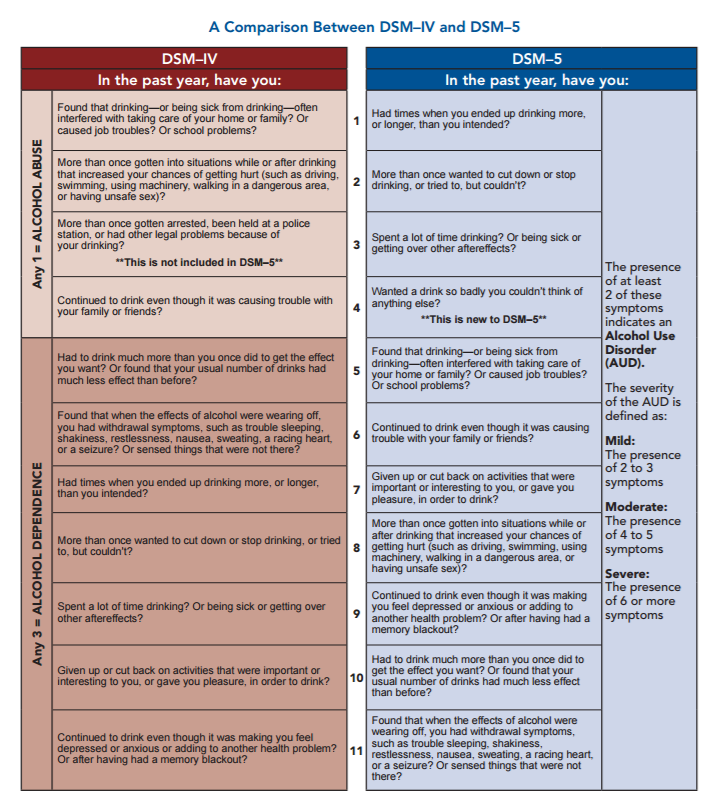
You can also experience psychosis with a number of health conditions.DSM-5 (formerly known as DSM-V) is the fifth edition of the American Psychiatric Association's (APA) Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. Other related conditions to schizophrenia include: It’s important to rule out any medical conditions or any other mental illnesses like bipolar disorder. Symptoms can include:ĭiagnosis is typically made through a thorough physical exam, interview, and psychiatric evaluation. Schizoaffective disorder is further classified into subtypes based on whether a person has only depressive episodes, or whether they also have manic episodes with or without depression. Mood disorders can include either mania or depression. Psychosis - which involves a loss of contact with reality - is often a component. This disorder has elements of both schizophrenia and mood disorders. Schizoaffective disorder is a separate and different condition from schizophrenia, but sometimes gets lumped in with it. It usually involves a combination of treatments such as:Ĭonditions related to schizophrenia Schizoaffective disorder Treatment should be headed by a child psychiatrist with experience in childhood schizophrenia. It’s crucial to rule out any other condition, including substance use or an organic medical issue.
Dsm 5 schizophrenia professional#
It’s important to have a knowledgeable professional make a diagnosis of childhood schizophrenia, because it’s so rare. As teens get older, more typical symptoms of schizophrenia like those in adults usually emerge. Younger individuals are less likely to have delusions, but they’re more likely to have hallucinations. Symptoms in older children and teens include: It’s important to rule out developmental issues when considering a very early-onset schizophrenia diagnosis. Symptoms in very young children are similar to those of developmental disorders, such as autism and attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). A diagnosis under the age of 13 is considered very early-onset, and is extremely rare. Early-onset schizophrenia typically occurs between the ages of 13 and 18. A diagnosis in children is fairly uncommon. It generally presents itself as immobility, but can also look like:Ĭhildhood schizophrenia isn’t a subtype, but rather used to refer to the time of diagnosis. This is because it occurs in a variety of psychiatric conditions and general medical conditions. Catatonic schizophreniaĪlthough catatonic schizophrenia was a subtype in the previous edition of the DSM, it’s been argued in the past that catatonia should be more of a specifier. Therefore, this designation is rarely used anymore. Many people with schizophrenia go through periods where their symptoms wax and wane and vary in frequency and intensity. Residual schizophrenia usually includes more “negative” symptoms, such as: The symptoms have generally lessened in intensity. It’s been used when a person has a previous diagnosis of schizophrenia but no longer has any prominent symptoms of the disorder. With the new diagnostic criteria, this merely signifies to the clinician that a variety of symptoms are present. For instance, an individual who had catatonic behavior but also had delusions or hallucinations, with word salad, might have been diagnosed with undifferentiated schizophrenia. Undifferentiated schizophrenia was the term used to describe when an individual displayed behaviors that were applicable to more than one type of schizophrenia.

Word salad is a verbal symptom where random words are strung together in no logical order.
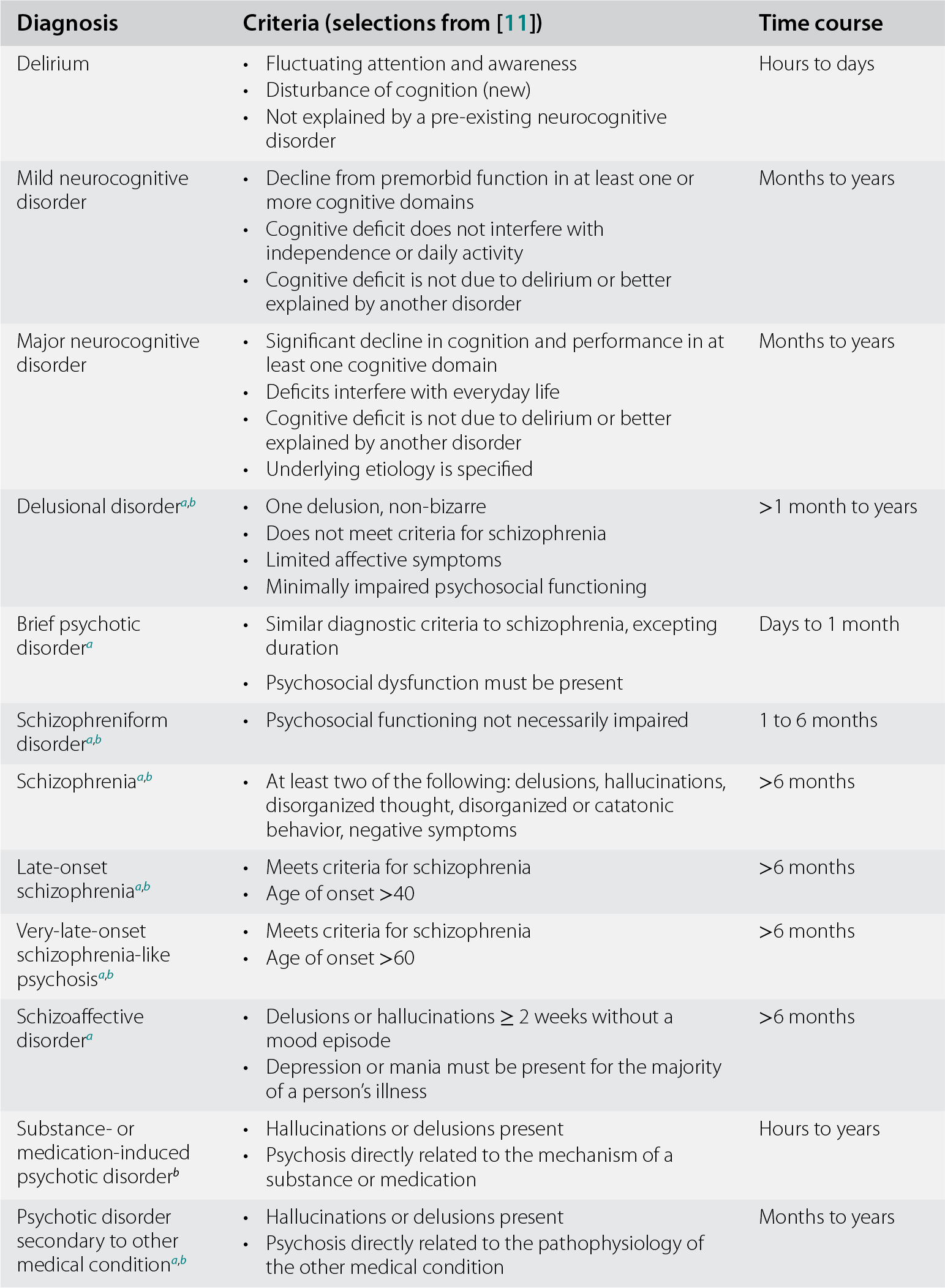
Hence, it was then just changed to schizophrenia. In 2013, the American Psychiatric Association determined that paranoia was a positive symptom of the disorder, so paranoid schizophrenia wasn’t a separate condition. Paranoid schizophrenia used to be the most common form of schizophrenia. Although the subtypes don’t exist as separate clinical disorders anymore, they can still be helpful as specifiers and for treatment planning.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
